Types of Forging Processes Explained
Types of Forging Processes Explained
Forging processes are manufacturing processes used to create strength and durability in metal components that are pressed using compressive forces. In the manufacturing of hand tools, forging is used to improve strength, impact force, and tool life by refining the metal’s grain structure.
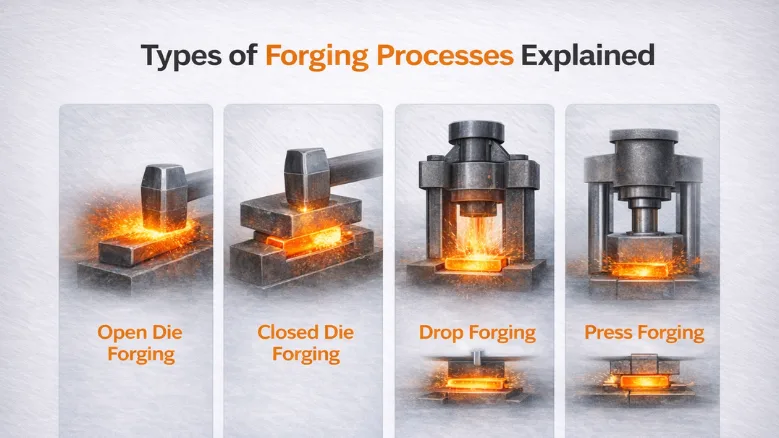
The main types of forging processes used in hand tool manufacturing include open die forging, closed die forging, drop forging, and press forging.
Open Die Forging
What Is Open Die Forging?
Open die forging is a forging method in which heated metal is shaped between flat or simple dies that do not fully enclose the material. The metal is progressively worked into shape through repeated compression.
How the Forging Process Works
In this method, force is applied directly to the exposed workpiece, allowing the material to spread and flow freely. The controlled deformation is beneficial for internal grain alignment while allowing room to shape large or simply shaped objects.
Relevance in Hand Tool Manufacturing
Open die forging is mainly used to produce tooling blanks or initial shapes where further machining is required. This process can be used when precision in dimensions is not a requirement, but strength is essential.
Key Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
- Improves internal grain structure
- Suitable for large or custom-shaped components
Limitations:
- Lower dimensional accuracy
- Limited direct use for finished hand tools
Key Highlight: Open Die Forging is best suited for strong tool blank materials but is not recommended for making precision hand tools.
Closed Die Forging
What is Closed Die Forging?
Closed die forging, also known as impression die forging, involves metal that is forged around precision-made molds that enclose the workpiece completely. The metal assumes the near-final shape as it flows into the mold.
How Hot Forging Enhances Tool Strength
This method is commonly carried out using hot forging, where elevated temperatures allow controlled metal flow and optimal grain alignment. The enclosed die design ensures uniform deformation and repeatable results.
Applications in Hand Tools
Closed die forging is widely used for spanners, wrenches, pliers, and similar hand tools that require consistent dimensions, high strength, and repeatable quality across large production volumes.
Key Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- High strength and dimensional consistency
- Ideal for mass production
Limitations:
- Higher tooling cost compared to open die forging
Key Highlight: Closed die forging offers an excellent balance of strength, precision, and consistency for most hand tools.
Drop Forging
What Is Drop Forging?
Drop forging is a type of closed die forging where a hammer repeatedly strikes heated metal to force it into the die shape. The impact energy compacts the material effectively.
How Impact Improves Tool Durability
Repeated hammering refines the grain flow along the shape of the tool, significantly improving toughness and fatigue resistance. This makes drop-forged tools highly resistant to cracking under stress.
Common Hand Tool Applications
Drop forging is commonly used for hammers, spanners, and other load-bearing or impact-prone tools that must withstand repeated shock during use.
Key Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- Excellent impact resistance
- Long service life under heavy use
Limitations:
- Higher energy and equipment requirements
Key Highlights: Drop forging is preferred for heavy-duty hand tools that face repeated impact and high stress.
Press Forging
What Is Press Forging?
Press forging uses continuous, controlled pressure rather than impact to shape heated metal within closed dies. The pressure is applied gradually and evenly.
How Controlled Pressure Improves Precision
The slower deformation allows uniform metal flow throughout the component, reducing internal stress and improving dimensional accuracy compared to impact-based forging methods.
Uses in Precision Hand Tools
Press forging is preferred for hand tools that require consistent thickness, smooth contours, and reliable strength across large production batches.
Key Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- High-dimensional accuracy
- Uniform material properties
Limitations:
- Slower production cycle compared to drop forging
Key Highlights: Press forging is ideal for precision hand tools where accuracy and consistency are critical.
Comparison of Forging Methods Used in Hand Tools
The table below compares common forging methods used in hand tools based on strength, precision, cost, and application.
| Forging Method | Strength Level | Precision | Cost Level | Common Hand Tools |
| Open Die Forging | Moderate | Low | Low | Tool blanks, large components |
| Closed Die Forging | High | High | Medium | Spanners, wrenches, pliers |
| Drop Forging | Very High | High | Medium | Hammers, heavy-duty tools |
| Press Forging | High | Very High | Higher | Precision hand tools |
This comparison highlights how different forging methods serve specific functional and performance requirements in hand tool manufacturing.
Why Forging Process Matters in Hand Tool Manufacturing
Forging processes directly influence a hand tool’s strength, durability, and user safety. Forging aligns the metal grain structure along the shape of the tool, improving load-bearing capacity and resistance to fatigue and fracture.
Forged tools perform reliably under vibration, impact, and repeated stress, making them suitable for professional and industrial environments. Consistent forging methods also ensure uniform quality across production batches, reducing performance variation and failure risk.
Choosing the Right Forging Method for Durable Hand Tools
Proper selection of forging technique depends upon the tool’s purpose, load conditions, and precision demands. For heavy-duty tools, forging processes can be beneficial if toughness and shock resistance are required, while precision instruments can use deformation control techniques.
Generally speaking, closed die forging and drop forging techniques are considered to be the most appropriate in manufacturing hand tools with high strength and durability.
The selection of a forging method is based on performance criteria, safety considerations, and service conditions that are applicable in the real world, rather than on considerations of cost savings.
Trusted Forging Practices at JCBL Hand Tools
At JCBL Hand Tools, the forging techniques applied are based strictly on the functional needs and working conditions of the tools. By employing genuine forging techniques and manufacturing disciplines, JCBL Hand Tools emphasizes satisfaction in the realms of strength and performance in hand tools.
Such a manufacturing-centric approach is relevant to the development of tools that satisfy the requirements of skilled professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
There are different forge mechanisms, but the most common forge techniques in the development of hand tools are open die forging, closed die forging, drop forging, and press forging. These techniques result in different standards of strength and precision.
Closed die forging as well as drop forging are generally employed in preference for most hand tools as these processes enable tools to exhibit maximum strength, quality, as well as durability.
In the drop forging method, the metal is heated and repeatedly hammered within closed dies to achieve the desired shape. As a result, the tools produced exhibit better grain flow and a longer life, with significant resistance to impact.
Unlike open die forging, which has lower initial tooling costs, closed die forging has higher initial costs but gives better precision, consistency, and strength; hence, such tools give good value in mass production of hand tools.
Drop forging usually offers the best level of durability since the grain structure is refined, making it less susceptible to impacts and fatigue; hence, it is best used for making hand tools.




